7. 在 Form1.cs 中,将以下代码:
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
}
替换为:
// Excel object references.
private Excel.Application m_objExcel = null;
private Excel.Workbooks m_objBooks = null;
private Excel._Workbook m_objBook = null;
private Excel.Sheets m_objSheets = null;
private Excel._Worksheet m_objSheet = null;
private Excel.Range m_objRange = null;
private Excel.Font m_objFont = null;
private Excel.QueryTables m_objQryTables = null;
private Excel._QueryTable m_objQryTable = null;
// Frequenty-used variable for optional arguments.
private object m_objOpt = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
// Paths used by the sample code for accessing and storing data.
private object m_strSampleFolder = "C:\\ExcelData\\";
private string m_strNorthwind = "C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office10\\Samples\\Northwind.mdb";
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
comboBox1.DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDownList;
comboBox1.Items.AddRange(new object[]{
"Use Automation to Transfer Data Cell by Cell ",
"Use Automation to Transfer an Array of Data to a Range on a Worksheet ",
"Use Automation to Transfer an ADO Recordset to a Worksheet Range ",
"Use Automation to Create a QueryTable on a Worksheet",
"Use the Clipboard",
"Create a Delimited Text File that Excel Can Parse into Rows and Columns",
"Transfer Data to a Worksheet Using ADO.NET "});
comboBox1.SelectedIndex = 0;
button1.Text = "Go!";
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
switch (comboBox1.SelectedIndex)
{
case 0 : Automation_CellByCell(); break;
case 1 : Automation_UseArray(); break;
case 2 : Automation_ADORecordset(); break;
case 3 : Automation_QueryTable(); break;
case 4 : Use_Clipboard(); break;
case 5 : Create_TextFile(); break;
case 6 : Use_ADONET(); break;
}
//Clean-up
m_objFont = null;
m_objRange = null;
m_objSheet = null;
m_objSheets = null;
m_objBooks = null;
m_objBook = null;
m_objExcel = null;
GC.Collect();
}
private void Automation_CellByCell()
{
// Start a new workbook in Excel.
m_objExcel = new Excel.Application();
m_objBooks = (Excel.Workbooks)m_objExcel.Workbooks;
m_objBook = (Excel._Workbook)(m_objBooks.Add(m_objOpt));
// Add data to cells of the first worksheet in the new workbook.
m_objSheets = (Excel.Sheets)m_objBook.Worksheets;
m_objSheet = (Excel._Worksheet)(m_objSheets.get_Item(1));
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A1", m_objOpt);
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,"Last Name");
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("B1", m_objOpt);
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,"First Name");
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A2", m_objOpt);
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,"Doe");
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("B2", m_objOpt);
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,"John");
// Apply bold to cells A1:B1.
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A1", "B1");
m_objFont = m_objRange.Font;
m_objFont.Bold=true;
// Save the workbook and quit Excel.
m_objBook.SaveAs(m_strSampleFolder + "Book1.xls", m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook.Close(false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objExcel.Quit();
}
private void Automation_UseArray()
{
// Start a new workbook in Excel.
m_objExcel = new Excel.Application();
m_objBooks = (Excel.Workbooks)m_objExcel.Workbooks;
m_objBook = (Excel._Workbook)(m_objBooks.Add(m_objOpt));
m_objSheets = (Excel.Sheets)m_objBook.Worksheets;
m_objSheet = (Excel._Worksheet)(m_objSheets.get_Item(1));
// Create an array for the headers and add it to cells A1:C1.
object[] objHeaders = {"Order ID", "Amount", "Tax"};
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A1", "C1");
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,objHeaders);
m_objFont = m_objRange.Font;
m_objFont.Bold=true;
// Create an array with 3 columns and 100 rows and add it to
// the worksheet starting at cell A2.
object[,] objData = new Object[100,3];
Random rdm = new Random((int)DateTime.Now.Ticks);
double nOrderAmt, nTax;
for(int r=0;r<100;r++)
{
objData[r,0] = "ORD" + r.ToString("0000");
nOrderAmt = rdm.Next(1000);
objData[r,1] = nOrderAmt.ToString("c");
nTax = nOrderAmt*0.07;
objData[r,2] = nTax.ToString("c");
}
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A2", m_objOpt);
m_objRange = m_objRange.get_Resize(100,3);
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,"objData");
// Save the workbook and quit Excel.
m_objBook.SaveAs(m_strSampleFolder + "Book2.xls", m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook.Close(false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objExcel.Quit();
}
private void Automation_ADORecordset()
{
// Create a Recordset from all the records in the Orders table.
ADODB.Connection objConn = new ADODB.Connection();
ADODB._Recordset objRS = null;
objConn.Open("Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" +
m_strNorthwind + ";", "", "", 0);
objConn.CursorLocation = ADODB.CursorLocationEnum.adUseClient;
object objRecAff;
objRS = (ADODB._Recordset)objConn.Execute("Orders", out objRecAff,
(int)ADODB.CommandTypeEnum.adCmdTable);
// Start a new workbook in Excel.
m_objExcel = new Excel.Application();
m_objBooks = (Excel.Workbooks)m_objExcel.Workbooks;
m_objBook = (Excel._Workbook)(m_objBooks.Add(m_objOpt));
m_objSheets = (Excel.Sheets)m_objBook.Worksheets;
m_objSheet = (Excel._Worksheet)(m_objSheets.get_Item(1));
// Get the Fields collection from the recordset and determine
// the number of fields (or columns).
System.Collections.IEnumerator objFields = objRS.Fields.GetEnumerator();
int nFields = objRS.Fields.Count;
// Create an array for the headers and add it to the
// worksheet starting at cell A1.
object[] objHeaders = new object[nFields];
ADODB.Field objField = null;
for(int n=0;n<nFields;n++)
{
objFields.MoveNext();
objField = (ADODB.Field)objFields.Current;
objHeaders[n] = objField.Name;
}
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A1", m_objOpt);
m_objRange = m_objRange.get_Resize(1, nFields);
m_objRange.set_Value(m_objOpt,objHeaders);
m_objFont = m_objRange.Font;
m_objFont.Bold=true;
// Transfer the recordset to the worksheet starting at cell A2.
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A2", m_objOpt);
m_objRange.CopyFromRecordset(objRS, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
// Save the workbook and quit Excel.
m_objBook.SaveAs(m_strSampleFolder + "Book3.xls", m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook.Close(false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objExcel.Quit();
//Close the recordset and connection
objRS.Close();
objConn.Close();
}
private void Automation_QueryTable()
{
// Start a new workbook in Excel.
m_objExcel = new Excel.Application();
m_objBooks = (Excel.Workbooks)m_objExcel.Workbooks;
m_objBook = (Excel._Workbook)(m_objBooks.Add(m_objOpt));
// Create a QueryTable that starts at cell A1.
m_objSheets = (Excel.Sheets)m_objBook.Worksheets;
m_objSheet = (Excel._Worksheet)(m_objSheets.get_Item(1));
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A1", m_objOpt);
m_objQryTables = m_objSheet.QueryTables;
m_objQryTable = (Excel._QueryTable)m_objQryTables.Add(
"OLEDB;Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" +
m_strNorthwind + ";", m_objRange, "Select * From Orders");
m_objQryTable.RefreshStyle = Excel.XlCellInsertionMode.xlInsertEntireRows;
m_objQryTable.Refresh(false);
// Save the workbook and quit Excel.
m_objBook.SaveAs(m_strSampleFolder + "Book4.xls", m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange, m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook.Close(false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objExcel.Quit();
}
private void Use_Clipboard()
{
// Copy a string to the clipboard.
string sData = "FirstName\tLastName\tBirthdate\r\n" +
"Bill\tBrown\t2/5/85\r\n" +
"Joe\tThomas\t1/1/91";
System.Windows.Forms.Clipboard.SetDataObject(sData);
// Start a new workbook in Excel.
m_objExcel = new Excel.Application();
m_objBooks = (Excel.Workbooks)m_objExcel.Workbooks;
m_objBook = (Excel._Workbook)(m_objBooks.Add(m_objOpt));
// Paste the data starting at cell A1.
m_objSheets = (Excel.Sheets)m_objBook.Worksheets;
m_objSheet = (Excel._Worksheet)(m_objSheets.get_Item(1));
m_objRange = m_objSheet.get_Range("A1", m_objOpt);
m_objSheet.Paste(m_objRange, false);
// Save the workbook and quit Excel.
m_objBook.SaveAs(m_strSampleFolder + "Book5.xls", m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange, m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook.Close(false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objExcel.Quit();
}
private void Create_TextFile()
{
// Connect to the data source.
System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection objConn = new System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection(
"Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" + m_strNorthwind + ";");
objConn.Open();
// Execute a command to retrieve all records from the Employees table.
System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand objCmd = new System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand(
"Select * From Employees", objConn);
System.Data.OleDb.OleDbDataReader objReader;
objReader = objCmd.ExecuteReader();
// Create the FileStream and StreamWriter object to write
// the recordset contents to file.
System.IO.FileStream fs = new System.IO.FileStream(
m_strSampleFolder + "Book6.txt", System.IO.FileMode.Create);
System.IO.StreamWriter sw = new System.IO.StreamWriter(
fs, System.Text.Encoding.Unicode);
// Write the field names (headers) as the first line in the text file.
sw.WriteLine(objReader.GetName(0) + "\t" + objReader.GetName(1) +
"\t" + objReader.GetName(2) + "\t" + objReader.GetName(3) +
"\t" + objReader.GetName(4) + "\t" + objReader.GetName(5));
// Write the first six columns in the recordset to a text file as
// tab-delimited.
while(objReader.Read())
{
for(int i=0;i<=5;i++)
{
if(!objReader.IsDBNull(i))
{
string s;
s = objReader.GetDataTypeName(i);
if(objReader.GetDataTypeName(i)=="DBTYPE_I4")
{
sw.Write(objReader.GetInt32(i).ToString());
}
else if(objReader.GetDataTypeName(i)=="DBTYPE_DATE")
{
sw.Write(objReader.GetDateTime(i).ToString("d"));
}
else if (objReader.GetDataTypeName(i)=="DBTYPE_WVARCHAR")
{
sw.Write(objReader.GetString(i));
}
}
if(i<5) sw.Write("\t");
}
sw.WriteLine();
}
sw.Flush(); // Write the buffered data to the FileStream.
// Close the FileStream.
fs.Close();
// Close the reader and the connection.
objReader.Close();
objConn.Close();
// ==================================================================
// Optionally, automate Excel to open the text file and save it in the
// Excel workbook format.
// Open the text file in Excel.
m_objExcel = new Excel.Application();
m_objBooks = (Excel.Workbooks)m_objExcel.Workbooks;
m_objBooks.OpenText(m_strSampleFolder + "Book6.txt", Excel.XlPlatform.xlWindows, 1,
Excel.XlTextParsingType.xlDelimited, Excel.XlTextQualifier.xlTextQualifierDoubleQuote,
false, true, false, false, false, false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook = m_objExcel.ActiveWorkbook;
// Save the text file in the typical workbook format and quit Excel.
m_objBook.SaveAs(m_strSampleFolder + "Book6.xls", Excel.XlFileFormat.xlWorkbookNormal,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt, Excel.XlSaveAsAccessMode.xlNoChange, m_objOpt, m_objOpt,
m_objOpt, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objBook.Close(false, m_objOpt, m_objOpt);
m_objExcel.Quit();
}
private void Use_ADONET()
{
// Establish a connection to the data source.
System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection objConn = new System.Data.OleDb.OleDbConnection(
"Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" + m_strSampleFolder +
"Book7.xls;Extended Properties=Excel 8.0;");
objConn.Open();
// Add two records to the table named 'MyTable'.
System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand objCmd = new System.Data.OleDb.OleDbCommand();
objCmd.Connection = objConn;
objCmd.CommandText = "Insert into MyTable (FirstName, LastName)" +
" values ('Bill', 'Brown')";
objCmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
objCmd.CommandText = "Insert into MyTable (FirstName, LastName)" +
" values ('Joe', 'Thomas')";
objCmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
// Close the connection.
objConn.Close();
}
} // End Class
}// End namespace
注意:您必须更改 Visual Studio 2005 中的代码。默认情况下,当创建一个 Windows 窗体项目时,Visual C# 会向该项目中添加一个窗体。该窗体被命名为 Form1。代表该窗体的两个文件被命名为 Form1.cs 和 Form1.designer.cs。您在 Form1.cs 中编写代码。Form1.designer.cs 文件是 Windows 窗体设计器编写代码的地方,这些代码可以实现通过拖放工具箱中的控件而执行的所有操作。
有关 Visual C# 2005 中的 Windows 窗体设计器的更多信息,请访问下面的 Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN) 网站:
http://msdn2.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/ms173077.aspx (http://msdn2.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/ms173077.aspx)
注意:如果您没有将 Office 安装到默认文件夹 (C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office) 中,请修改代码示例中的“m_strNorthwind”常量以匹配 Northwind.mdb 的安装路径。
8. 将下面的代码添加到 Form1.cs 中的“Using”指令中:
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
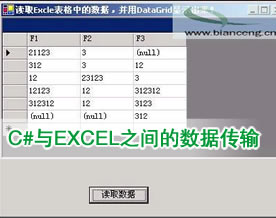
9. 按 F5 生成并运行该示例。
© 2021-现在 好学IT学院 软著登记号:2025SR2204462 湘ICP备2022000939号|